The Gambia government confirmed an outbreak of mpox following the detection of a single case on July 18, 2025
This incident, announced on July 23, 2025, coincides with a broader surge in mpox cases across West Africa, with neighboring countries like Sierra Leone, Liberia, Guinea, DRC, Uganda, and Burundi reporting significant increases.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has maintained that mpox remains an international health emergency, highlighting the ongoing challenges in controlling the disease. As of today, Wednesday, July 23, 2025, at 11:50 AM WAT, this note explores the outbreak’s details, regional context, and implications, drawing from the provided text.
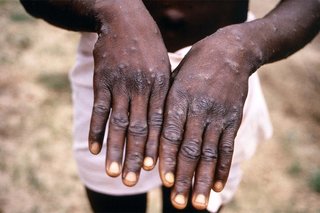
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, part of the same family as smallpox. First detected in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), it spreads through close physical contact with infected individuals or animals, causing symptoms like fever, muscle aches, and large, boil-like skin lesions. It can be deadly, particularly for vulnerable groups such as children, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems.
The virus has two subtypes: clade 1 and clade 2, with sequencing ongoing in The Gambia to determine the subtype, which could affect transmission dynamics and response strategies.
The WHO declared mpox an international health emergency in August 2024 due to a surge in cases, particularly clade I in DRC and neighboring countries, and reiterated this status in June 2025 amid rising cases in West Africa.
This context frames The Gambia’s outbreak, which is part of a regional trend of increasing infections, with significant case numbers reported in the provided data.
Outbreak Details in The Gambia.
The Gambian Ministry of Health confirmed the outbreak on July 23, 2025, stating that a single case was detected on July 18, 2025, through the routine surveillance system.
The ministry emphasized that detecting one case in a country where mpox is not presently circulating constitutes an outbreak, requiring an immediate response.
They are actively searching for additional cases, conducting contact tracing, and engaging with communities to prevent further spread.
Sequencing is underway to determine the virus subtype, which is crucial for tailoring public health measures.
This outbreak is significant as it marks The Gambia’s first reported mpox case, highlighting the disease’s potential to spread rapidly in new areas.
The ministry’s proactive measures, including contact tracing and community engagement, are critical for containment, but the situation remains fluid, with the risk of additional cases depending on transmission chains and regional dynamics.
Regional Context and Comparative Data
The outbreak in The Gambia is part of a broader regional surge in West Africa. Here’s a detailed breakdown of recent case numbers in nearby countries, based on the provided information:
Country
Cases (Period)
Deaths
Sierra Leone
3,350 (Jan–late May 2025)
16
Significant contributor to regional outbreak
Liberia
71 active (early June 2025)
–
Reported active cases, no deaths specified
DRC
Thousands (2025)
–
Accounts for significant global burden
Uganda
Thousands (2025)
–
Part of regional surge, clade I concerns
Burundi
Thousands (2025)
–
Recent cases linked to DRC
This lists underscores the regional context, with Sierra Leone and Liberia particularly affected, contributing to the WHO’s emergency declaration.
The Gambia’s outbreak, while starting with a single case, is a concern given its proximity to these high-case areas, increasing the risk of cross-border transmission.
Public Health Measures and International Response
The Gambian government’s response includes active case finding, contact tracing, and community engagement, aligning with WHO recommendations for outbreak control.
The WHO’s declaration of mpox as an international health emergency in June 2025 has prompted calls for enhanced surveillance, vaccination efforts, and public awareness campaigns across Africa, though specific details for The Gambia were not mentioned in the provided text.
The provided information highlights the WHO’s role in classifying mpox as an emergency, with the ministry’s actions reflecting a coordinated approach.
However, challenges like vaccine access and border controls were not detailed, suggesting a focus on immediate containment rather than long-term strategies.
Implications and Public Sentiment
The outbreak in The Gambia raises concerns about the disease’s spread in a new area, potentially straining health systems and requiring international support.
The provided text does not include direct public sentiment, but the context of the WHO’s emergency status and regional case surges suggests global awareness and concern.
The controversy lies in response strategies, with debates over vaccine distribution, border controls, and aid delivery, especially given the impact on vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women.